Page 9 - Spec Tech Vol 1 Issue 08
P. 9
SPACE SENSORS
The imager was developed, tested, and Web by the NOAA National Geophysical
calibrated by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Data Center, also in Boulder.
Center in Huntsville, Ala., in conjunction with The imager will provide continuous, near
the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in realtime observation of the Sun’s corona,
Greenbelt, Md., NOAA, and the Air Force.
acquiring a full-disk image every minute.
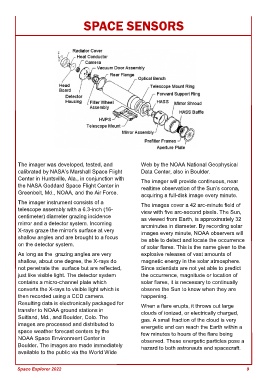
The imager instrument consists of a The images cover a 42 arc-minute field of
telescope assembly with a 6.3-inch (16- view with five arc-second pixels. The Sun,
centimeter) diameter grazing incidence as viewed from Earth, is approximately 32
mirror and a detector system. Incoming arcminutes in diameter. By recording solar
X-rays graze the mirror's surface at very images every minute, NOAA observers will
shallow angles and are brought to a focus be able to detect and locate the occurrence
on the detector system.
of solar flares. This is the name given to the
As long as the grazing angles are very explosive releases of vast amounts of
shallow, about one degree, the X-rays do magnetic energy in the solar atmosphere.
not penetrate the surface but are reflected, Since scientists are not yet able to predict
just like visible light. The detector system the occurrence, magnitude or location of
contains a micro-channel plate which solar flares, it is necessary to continually
converts the X-rays to visible light which is observe the Sun to know when they are
then recorded using a CCD camera. happening.
Resulting data is electronically packaged for When a flare erupts, it throws out large
transfer to NOAA ground stations in clouds of ionized, or electrically charged,
Suitland, Md., and Boulder, Colo. The gas. A small fraction of the cloud is very
images are processed and distributed to energetic and can reach the Earth within a
space weather forecast centers by the few minutes to hours of the flare being
NOAA Space Environment Center in observed. These energetic particles pose a
Boulder. The images are made immediately hazard to both astronauts and spacecraft.
available to the public via the World Wide
Space Explorer 2022 9